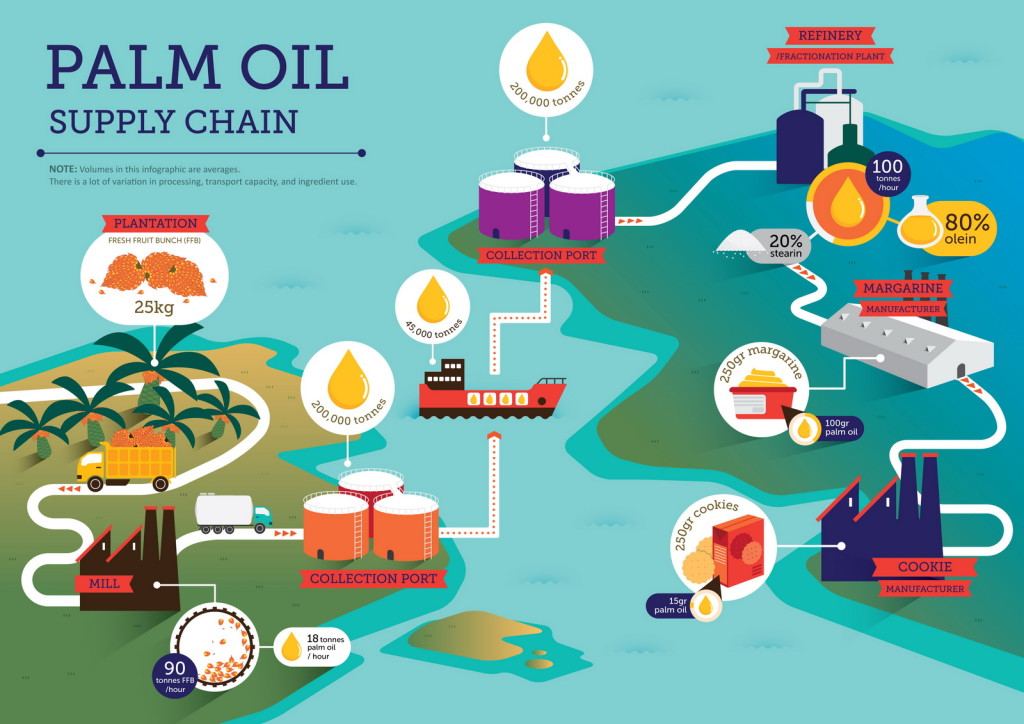
The global palm oil supply chain is a complex network that involves multiple stages, from cultivation and harvesting in tropical regions to processing, refining, and distribution to markets worldwide.
Key producers like Indonesia and Malaysia dominate the market, while major consumers include China, India, and the European Union. This intricate supply chain relies on efficient logistics, stable political environments, and favorable climatic conditions.
Any disruption in these elements can significantly impact the supply and demand balance, leading to price fluctuations and market instability.
Recent Disruptions: Analysis of Events Like the COVID-19 Pandemic, Natural Disasters, and Political Instability
1. COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has been one of the most significant disruptors of the global palm oil supply chain. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and labor shortages affected every stage of the supply chain:
- Labor Shortages: Plantations faced severe labor shortages due to movement restrictions and health concerns, leading to reduced harvesting and processing capacity.
- Logistics and Transportation: Restrictions on transportation and port operations disrupted the movement of palm oil, causing delays and increasing costs.
- Demand Fluctuations: While demand from the food industry remained relatively stable, the demand for palm oil in the biofuel sector fluctuated due to changes in energy consumption patterns.
- Natural Disasters Natural disasters such as floods, droughts, and storms have a profound impact on palm oil production:
- Floods: Excessive rainfall and flooding in key producing regions can damage plantations, reduce yield, and disrupt harvesting and transportation.
- Droughts: Prolonged droughts can stress palm oil trees, reducing productivity and leading to lower oil yields.
- Storms: Severe storms can cause physical damage to plantations and infrastructure, further disrupting the supply chain.
2. Political Instability
Political instability in producing countries can lead to disruptions in palm oil supply:
- Trade Policies: Changes in trade policies, such as export restrictions or tariffs, can alter the flow of palm oil in global markets, affecting prices.
- Land Conflicts: Political conflicts and land disputes can lead to disruptions in plantation operations, affecting production volumes.
- Regulatory Changes: Sudden changes in environmental regulations or labor laws can impact production practices and costs.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Strategies to Build Resilience and Manage Disruptions Effectively Building resilience in the palm oil supply chain is crucial to managing disruptions and ensuring stable supply and prices.
3. Diversification
Diversifying supply sources can reduce dependency on a single region or country, mitigating the impact of localized disruptions:
- Geographic Diversification: Encouraging production in multiple regions can spread risk and ensure continuous supply even if one region is affected.
- Supplier Diversification: Partnering with multiple suppliers can provide flexibility and alternative sourcing options during disruptions.
4. Technological Innovations
Implementing technological innovations can enhance supply chain efficiency and resilience:
- Precision Agriculture: Using technology to monitor crop health, optimize inputs, and predict yields can improve productivity and reduce vulnerability to environmental factors.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can enhance transparency and traceability in the supply chain, ensuring better coordination and quicker responses to disruptions.
5. Risk Management Practices
Adopting robust risk management practices can help mitigate the impact of supply chain disruptions:
- Inventory Management: Maintaining adequate inventory levels can buffer against supply shocks and ensure continuity in production and distribution.
- Contractual Agreements: Long-term contracts with flexible terms can provide stability and predictability in supply and pricing.
- Insurance: Investing in insurance policies that cover natural disasters and political risks can protect against financial losses.
- Price Implications: How Supply Chain Disruptions Affect the Supply, Demand, and Prices of Palm Oil
6. Supply Impacts
Disruptions in the supply chain can lead to a reduced availability of palm oil, creating supply shortages. When supply is constrained, it can result in:
- Increased Prices: Limited supply coupled with steady or rising demand can lead to significant price increases.
- Volatility: Unpredictable supply disruptions can cause price volatility, making it difficult for stakeholders to plan and budget effectively.
7. Demand Impacts
While supply disruptions often lead to price increases, they can also influence demand:
- Substitution Effect: High prices may lead consumers and industries to substitute palm oil with other vegetable oils, potentially reducing demand.
- Market Adaptations: In response to high prices, some industries may reformulate products or adjust production processes to reduce reliance on palm oil.
8. Market Dynamics
The interplay between supply and demand in the face of disruptions creates complex market dynamics:
- Speculation: Uncertainty and potential supply shortages can lead to speculative trading, further driving up prices.
- Policy Responses: Governments may implement policies such as subsidies, tariffs, or export restrictions to stabilize domestic markets, influencing global prices.
Conclusion
Global supply chain disruptions have a profound impact on palm oil prices, affecting supply, demand, and market stability.
The complexity of the palm oil supply chain makes it particularly vulnerable to events such as the COVID-19 pandemic, natural disasters, and political instability. Building resilience through diversification, technological innovation, and robust risk management practices is essential to mitigate these impacts.
Understanding the price implications of supply chain disruptions can help stakeholders navigate market uncertainties and ensure a more stable and sustainable palm oil industry.