Factors that Can Affect Wireless Network Speed and How to Measure Them
Wireless networks are computer networks that use radio waves to transmit data between devices. Wireless networks allow for greater flexibility and mobility than wired networks, which require physical cables to connect devices. They have become increasingly popular in homes, businesses, and public spaces due to their convenience and ease of use.
The speed of a wireless network is crucial for ensuring that data can be transmitted quickly and efficiently between devices. Slow network speeds can lead to frustratingly long website load times, dropped calls during online meetings, and laggy online gaming experiences. Therefore, a fast and reliable wireless network is essential for personal and professional use.
The purpose of this article is to explore the various factors that can affect the speed of a wireless network and how to measure them. We will also provide tips on improving network speed, so you can have a fast and reliable wireless network that meets your needs.
Factors Affecting Wireless Network Speed
A. Distance from the Router
One of the most significant factors affecting wireless network speed is the distance between your device and the wireless router. The farther away you are from the router, the weaker the signal and the slower your connection speed will be. Walls and other obstacles can also weaken the signal, so it’s important to consider the placement of your router and the location of your devices.
B. Obstructions
Physical obstructions like walls, furniture, and appliances can also impact wireless network speed. If the signal has to pass through walls or other obstacles, the strength of the signal will be reduced, resulting in a slower connection speed.
C. Wireless Interference
Wireless interference from other devices can also impact network speed. Devices such as cordless phones, baby monitors, and microwaves can interfere with the wireless signal, leading to slower connection speeds.
D. Network Congestion
Network congestion occurs when too many devices are trying to access the network simultaneously. This can slow down the network speed, especially during peak usage times. This can be a particular problem in crowded public spaces, such as airports or cafes.
E. Outdated Equipment
Outdated or poorly configured equipment, such as routers or network adapters, can also impact wireless network speed. Older equipment may not support the latest wireless standards or be unable to handle high-speed connections.
Measuring Wireless Network Speed
A. Understanding Bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data transmitted over a network in a given period. Bandwidth is typically measured in megabits per second (Mbps) and is critical to determining network speed. The higher the bandwidth, the faster the network speed will be.
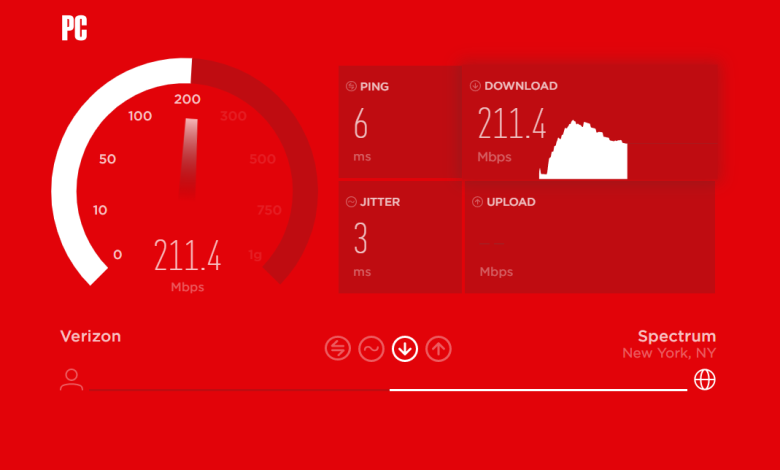
B. Tools for Measuring Network Speed
Online Speed Tests
Online speed tests are a popular way to measure network speed. These tests typically involve accessing a website and clicking a button to initiate a test. The test will measure your network connection’s upload and download speeds and provide a report of the results.
Many websites offer online speed tests, such as Speedtest.net and Fast.com. These tests are easy to use and provide a quick way to measure your network speed.
Network Monitoring Software
Network monitoring software is another option for measuring network speed. This software is typically installed on a computer or device and provides real-time network activity monitoring. This can be useful for identifying network use patterns and pinpointing areas where network speed may be a problem.
Examples of network monitoring software include PRTG Network Monitor, SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, and Nagios Core. These tools can provide more detailed information about network speed than online speed tests and can be useful for troubleshooting network issues.
Interpreting the Results
When interpreting the results of network speed tests, it’s essential to consider factors such as the time of day, the number of devices on the network, and the type of activity being performed. For example, streaming video may require more bandwidth than browsing the web, so network speed may vary depending on the activity type.
Learn More About Megabits Unit Storage Capacity
Improving Wireless Network Speed
A. Upgrading Equipment
Upgrading your equipment can be an effective way to improve your wireless network speed. This can include upgrading your router, network adapters, or other network hardware. Newer equipment will typically support the latest wireless standards and offer faster connection speeds.
B. Reducing wireless interference
Reducing wireless interference can also improve your network speed. This can include placing your router in a location with fewer obstacles, using devices that operate on different frequencies, or moving devices that may be causing interference away from your router.
C. Adjusting router settings
Adjusting your router settings can also help to improve network speed. This can include changing the channel that your router is operating on, adjusting the transmit power, or configuring Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize certain types of network traffic.
D. Changing the wireless channel
Changing the wireless channel that your router is operating on can also help to improve network speed. By default, most routers operate on either channel 1, 6, or 11. However, these channels can become congested, leading to slower network speeds. Changing to a less congested channel can help to improve network speed.
E. Limiting the number of devices on the network
Limiting the number of devices on the network can also help to improve network speed. Network congestion can occur when too many devices try to access the network simultaneously, leading to slower speeds. Limiting the number of devices on the network can reduce congestion and improve network speed.
Conclusion
This article discussed several factors affecting wireless network speed, including distance from the router, obstructions, wireless interference, network congestion, and outdated equipment. By understanding these factors, you can identify potential issues and take steps to improve your network speed.
We also discussed various tools and techniques for measuring and improving network speed. These included online speed tests, network monitoring software, upgrading equipment, reducing wireless interference, adjusting router settings, changing wireless channels, and limiting the number of devices on the network.
Maintaining a fast wireless network is essential for many modern activities, from streaming videos and playing games to conducting video conferences and accessing cloud services. Following the tips and techniques discussed in this article can improve your network speed and enjoy a more reliable and faster wireless network. Read also!



